Reasons of erectile dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a prevalent condition characterized by the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual performance. It can have a significant impact on a man's self-esteem, relationships, and overall quality of life. Understanding the common causes and risk factors of ED is essential for effective prevention and management of this condition.
One of the primary causes of ED is poor blood flow to the penis. This can be the result of various underlying health conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease. These conditions can damage the blood vessels and restrict the flow of blood, impairing the ability to achieve an erection. Additionally, obesity and a sedentary lifestyle can contribute to poor blood flow and increase the risk of ED.
Psychological factors also play a significant role in the development of ED. Stress, anxiety, depression, and relationship issues can all contribute to performance anxiety and affect sexual function. Psychological factors can act as both a cause and a consequence of ED, creating a vicious cycle that worsens the condition.
Other common causes and risk factors of ED include hormonal imbalances, such as low testosterone levels, as well as certain medications and substance abuse. Age is also a significant risk factor, as the prevalence of ED increases with age. However, it is essential to note that while aging may increase the risk, ED is not an inevitable part of getting older.
By addressing these common causes and risk factors, individuals can reduce their chances of developing ED or manage the condition effectively. Healthy lifestyle choices, regular exercise, managing stress, and seeking treatment for underlying health conditions are all important steps in preventing and treating erectile dysfunction.
What Causes Erectile Dysfunction?
Erectile dysfunction, also known as impotence, can be caused by a variety of factors. Understanding the underlying causes of erectile dysfunction can help in the diagnosis and treatment of this condition.
Physical Causes
Erectile dysfunction can be caused by physical factors such as vascular diseases, hormonal imbalances, nerve damage, or side effects of certain medications. Vascular diseases, such as atherosclerosis, can lead to reduced blood flow to the penis, resulting in difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection. Hormonal imbalances, particularly low testosterone levels, can also contribute to erectile dysfunction. Additionally, nerve damage, whether from injury or diseases like diabetes, can interfere with the transmission of signals necessary for penile erection.
Psychological Causes
Psychological factors can also play a significant role in erectile dysfunction. Stress, anxiety, depression, and relationship problems can all contribute to difficulties in achieving or maintaining an erection. Performance anxiety, in particular, is a common psychological cause of erectile dysfunction, where an individual becomes anxious about their ability to perform sexually.
Lifestyle Factors
Unhealthy lifestyle choices can also contribute to erectile dysfunction. This includes smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and drug abuse. These substances can affect blood flow and neurological functions, leading to difficulties in achieving or sustaining an erection. Obesity and a sedentary lifestyle can also contribute to erectile dysfunction by reducing blood flow throughout the body, including to the penis. Additionally, not getting enough exercise or sleep can impact hormonal balance and overall sexual health.
Other Causes
There are other potential causes of erectile dysfunction, including certain medical conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and kidney disease. These conditions can directly or indirectly affect blood flow and nerve function, leading to erectile dysfunction. Furthermore, undergoing surgery or radiation treatments in the pelvic area can damage blood vessels and nerves, resulting in erectile dysfunction.
In conclusion, erectile dysfunction can have a variety of causes, including physical, psychological, lifestyle, and medical factors. It is important for individuals experiencing erectile dysfunction to consult with a healthcare professional to identify the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Medical Conditions
1. Cardiovascular Disease
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is often associated with cardiovascular disease, which affects the heart and blood vessels. Conditions such as high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease can lead to reduced blood flow to the penis, making it difficult to achieve or maintain an erection. Additionally, the medications used to treat these conditions, such as beta blockers and diuretics, can also contribute to ED.
2. Diabetes
Diabetes is a medical condition characterized by high blood sugar levels. It can damage the blood vessels and nerves that are essential for normal erectile function. Men with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing erectile dysfunction compared to those without the condition. Poorly controlled blood sugar levels can further exacerbate the problem.
3. Neurological Disorders
Neurological disorders can also contribute to erectile dysfunction. Conditions such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, and spinal cord injuries can interfere with the normal functioning of the nerves involved in sexual arousal and erection. Damage to the nerves can disrupt the communication between the brain and the penis, making it difficult to achieve or maintain an erection.
4. Hormonal Imbalance
Hormonal imbalances, particularly low levels of testosterone, can contribute to erectile dysfunction. Testosterone is an important hormone for male sexual function, and reduced levels can affect libido and erection quality. Hormonal imbalances can be caused by conditions such as hypogonadism, obesity, and certain medications.
5. Kidney Disease
Kidney disease can affect erectile function due to the buildup of toxins and waste products in the body. The kidneys play a vital role in filtering waste from the blood, and when they are not functioning properly, it can lead to erectile dysfunction. Additionally, the medications used to treat kidney disease, such as diuretics and ACE inhibitors, can also contribute to ED.
In conclusion, many medical conditions can contribute to erectile dysfunction. It is important to address these underlying health issues to improve sexual function and overall well-being. Consulting with a healthcare professional is recommended to determine the most suitable treatment plan for individuals experiencing erectile dysfunction.
Medications and Treatments
Medications
Erectile dysfunction can be caused or aggravated by certain medications. Some common medications that may contribute to erectile dysfunction include:
- Antidepressants: Certain types of antidepressant medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), can interfere with sexual function and lead to erectile dysfunction.
- Antihypertensive drugs: Some medications used to treat high blood pressure, such as beta blockers and diuretics, can contribute to erectile dysfunction.
- Antihistamines: Certain antihistamine medications, such as diphenhydramine, can have negative effects on sexual function and contribute to erectile dysfunction.
- Prostate cancer treatments: Certain treatments for prostate cancer, such as radiation therapy and hormone therapy, can affect erectile function.
If you suspect that your medication may be causing or worsening your erectile dysfunction, it is important to speak with your healthcare provider. They may be able to adjust your medication or provide alternative options that do not have sexual side effects.
Treatments
There are several treatments available for erectile dysfunction, including:
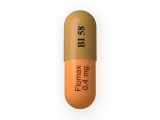
- Oral medications: Medications such as sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), and vardenafil (Levitra) can help improve erectile function by increasing blood flow to the penis.
- Injections: Certain medications can be injected directly into the base of the penis to achieve an erection. This method is often effective for men who do not respond well to oral medications.
- Vacuum erection devices: These devices create a vacuum around the penis, pulling blood into the organ to create an erection. A constriction band is then placed at the base of the penis to maintain the erection.
- Surgical implants: In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to implant devices that can help achieve and maintain an erection. These implants can be inflatable or malleable, depending on the needs of the individual.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment option for your individual needs and preferences.
Lifestyle Factors
Erectile dysfunction can be caused by a variety of lifestyle factors that contribute to poor blood circulation and overall health. These lifestyle factors can include:
- Poor diet: A diet that is high in processed foods, saturated fats, and refined sugars can contribute to obesity, high blood pressure, and diabetes, all of which are risk factors for erectile dysfunction.
- Lack of exercise: A sedentary lifestyle can lead to weight gain, muscle loss, and decreased blood flow, all of which can contribute to erectile dysfunction.
- Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and impairs blood flow, which can lead to erectile dysfunction.
- Excessive alcohol consumption: Heavy drinking can damage the liver, impair hormone production, and decrease testosterone levels, all of which can contribute to erectile dysfunction.
- Drug use: Certain recreational drugs, such as cocaine and amphetamines, can constrict blood vessels and interfere with nerve signals, leading to erectile dysfunction. Prescription medications, such as antidepressants and blood pressure medications, can also have side effects that contribute to erectile dysfunction.
- Stress and anxiety: Chronic stress and anxiety can lead to hormonal imbalances, high blood pressure, and poor blood flow, all of which can contribute to erectile dysfunction.
It is important to address these lifestyle factors in order to improve overall health and reduce the risk of developing erectile dysfunction. Making changes to diet, increasing physical activity, quitting smoking, moderating alcohol consumption, and seeking treatment for stress and anxiety can all have a positive impact on sexual health.
Psychological Factors
Erectile dysfunction (ED) can often be caused or exacerbated by psychological factors. These factors can include stress, anxiety, depression, and relationship problems.
Stress: High levels of stress can interfere with the body's ability to achieve and maintain an erection. Stress can lead to increased levels of cortisol, a hormone that can inhibit erections. Additionally, stress can affect the mind and cause distractions or preoccupations that make it difficult to become sexually aroused.
Anxiety: Anxiety can contribute to erectile dysfunction by creating a cycle of worry and performance anxiety. The fear of not being able to achieve or maintain an erection can actually make it more difficult to do so. Anxiety can also lead to a decrease in sexual desire, making it challenging to become sexually aroused.
Depression: Depression can have a profound impact on sexual function, including erectile dysfunction. The low mood and lack of interest in pleasurable activities associated with depression can make it difficult to feel sexually aroused. Additionally, some antidepressant medications can also contribute to erectile dysfunction.
Relationship problems: Difficulties in a relationship can often manifest as erectile dysfunction. Disagreements, unresolved conflicts, lack of communication, and emotional distance can all contribute to performance issues in the bedroom. The emotional state of a relationship can significantly impact a person's ability to achieve and maintain an erection.
It is important to note that psychological factors can often be intertwined with physical causes of erectile dysfunction. Addressing both the physical and psychological aspects of the condition is essential in effectively treating and managing ED.
Age and Hormonal Changes
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common condition that affects men of all ages, but the risk of developing it increases with age. As men get older, hormonal changes in their bodies can have an impact on their sexual function. Testosterone, the primary male sex hormone, naturally decreases with age, which can lead to decreased sexual desire and difficulties in achieving and maintaining an erection.
Age-related hormonal changes can also affect the blood vessels and nerves that are involved in the process of getting an erection. As men age, the blood vessels in the penis may become less responsive to signals from the brain, resulting in reduced blood flow and difficulties in achieving and sustaining an erection. Additionally, age-related nerve damage can also interfere with the transmission of signals between the brain and the penis, further contributing to erectile dysfunction.
In addition to age-related hormonal changes, other factors such as chronic medical conditions, lifestyle choices, and medications can also contribute to the development of erectile dysfunction. Men who have underlying health conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease, or obesity may be at an increased risk of developing ED. Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and a sedentary lifestyle can also contribute to the development of this condition.
It's important for men to be aware of the potential risk factors for erectile dysfunction and to take steps to maintain their sexual health as they age. This may include making lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, reducing alcohol consumption, exercising regularly, and managing chronic health conditions. Seeking medical advice and treatment options, such as hormone replacement therapy or medications, can also be beneficial in managing age-related hormonal changes and erectile dysfunction.
Other Risk Factors
Obesity
Being overweight or obese can contribute to the development of erectile dysfunction. Excess body weight can lead to hormonal imbalances, such as lower testosterone levels, which can affect sexual function. Additionally, obesity can cause cardiovascular problems, including high blood pressure and atherosclerosis, which can impede blood flow to the penis and hinder the ability to achieve or maintain an erection.
Sedentary Lifestyle
A sedentary lifestyle, characterized by a lack of physical activity, can increase the risk of erectile dysfunction. Regular exercise promotes healthy blood flow and cardiovascular function, which are essential for maintaining erectile function. In contrast, a sedentary lifestyle can lead to poor circulation and cardiovascular problems, which can impair erectile function.
Stress and Psychological Factors
Psychological factors, such as stress, anxiety, depression, and relationship problems, can contribute to the development of erectile dysfunction. Stress and anxiety can lead to high levels of cortisol, a stress hormone, which can interfere with the production of testosterone and affect sexual function. Additionally, psychological factors can cause performance anxiety and negatively impact sexual confidence and arousal.
Smoking
Smoking tobacco can increase the risk of erectile dysfunction. The chemicals in tobacco can damage blood vessels, restrict blood flow, and impair the ability to achieve or maintain an erection. Smoking is also associated with other health problems, such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes, which are common causes of erectile dysfunction.
Alcohol and Substance Abuse
Excessive alcohol consumption and substance abuse can contribute to erectile dysfunction. Alcohol can affect the nervous system and impair sexual function. Additionally, substance abuse can lead to hormonal imbalances and interfere with the production of testosterone, which can affect erectile function.
Medications and Medical Conditions
Certain medications, such as those used to treat high blood pressure, depression, and prostate conditions, can cause erectile dysfunction as a side effect. Additionally, medical conditions, such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and neurological disorders, can increase the risk of erectile dysfunction due to their impact on blood circulation and nerve function.
Follow us on Twitter @Pharmaceuticals #Pharmacy
Subscribe on YouTube @PharmaceuticalsYouTube




Be the first to comment on "Reasons of erectile dysfunction"