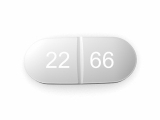
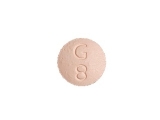
What happens if i take too much prednisone
Prednisone is a commonly prescribed corticosteroid medication that is used to reduce inflammation in the body. While it can be beneficial in treating a variety of conditions, taking excessive amounts of prednisone can have serious consequences on the body.
One of the main concerns with excessive prednisone use is the suppression of the immune system. Prednisone works by suppressing the immune response, which can make individuals more susceptible to infections. This can lead to an increased risk of developing bacterial, viral, and fungal infections, as well as a decreased ability to fight off these infections.
Excessive use of prednisone can also have a negative impact on bone health. Corticosteroids like prednisone can decrease the body's ability to absorb calcium and increase the excretion of calcium from the bones. This can lead to a decrease in bone density and an increased risk of developing osteoporosis.
In addition, long-term use of prednisone can cause a variety of cardiovascular problems. It can increase blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and the risk of developing blood clots. These factors can contribute to the development of cardiovascular diseases, such as heart attacks and strokes.
Furthermore, excessive prednisone use has been associated with mental health issues. It can cause mood swings, anxiety, depression, and insomnia. These psychological side effects can have a significant impact on an individual's overall well-being and quality of life.
It is important to note that these consequences typically occur with long-term or high-dose prednisone use. However, even short-term use of prednisone can have some of these effects on the body. If you are prescribed prednisone, it is critical to follow your doctor's instructions and not exceed the recommended dosage to minimize the risk of experiencing these detrimental consequences.
The Hidden Dangers of Excessive Prednisone Intake
Prednisone is a medication that is commonly prescribed to treat a variety of conditions, including inflammation, allergies, and autoimmune disorders. While it can be highly effective in treating these conditions, taking excessive amounts of prednisone can have serious consequences on one's health.
1. Weakening of the immune system
One of the main dangers of excessive prednisone intake is its effect on the immune system. Prednisone is a corticosteroid that works by suppressing the immune response, reducing inflammation and managing symptoms. However, taking too much prednisone can lead to a weakened immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections and illnesses.
2. Increased risk of osteoporosis
Another concern with excessive prednisone intake is its impact on bone health. Prolonged use of prednisone can lead to decreased bone density and increased risk of osteoporosis. This is especially worrisome for individuals who already have other risk factors for osteoporosis, such as being older or postmenopausal.
3. Metabolic changes and weight gain
Excessive prednisone intake can also disrupt normal metabolic function and lead to weight gain. Prednisone can increase appetite, cause fluid retention, and redistribute fat in the body. These effects can result in weight gain, especially in the abdominal area.
4. Mood changes and psychological effects
Prednisone can also have significant psychological effects on individuals who take it in excessive amounts. Mood swings, irritability, anxiety, and depression are common side effects of prednisone. These psychological changes can have a significant impact on a person's quality of life and overall well-being.
In summary, while prednisone can be an effective medication for treating certain conditions, taking excessive amounts of it can have serious consequences on one's health. It is important for individuals to follow their healthcare provider's instructions when using prednisone and to be aware of the potential risks associated with its excessive intake.
Understanding the Risks
Taking excessive prednisone, a powerful synthetic corticosteroid, can have a range of potential consequences, some of which can be severe and long-lasting. It is important to be aware of the risks associated with this medication in order to make informed decisions about its use.
Side Effects
One of the immediate risks of taking excessive prednisone is the potential for a variety of side effects. These can include weight gain, fluid retention, increased appetite, mood swings, difficulty sleeping, and increased vulnerability to infections. Prolonged use of prednisone can also lead to thinning of the skin, easy bruising, and slow wound healing.
Bone Loss
Prednisone can also have long-term consequences on bone health. Prolonged use of this medication can lead to a decrease in bone density, making individuals more prone to fractures and osteoporosis. Regular monitoring of bone health and taking preventive measures, such as calcium and vitamin D supplementation, can help minimize these risks.
Adrenal Suppression
Taking excessive prednisone can also suppress the normal functioning of the adrenal glands, which produce hormones that help regulate the body's response to stress and inflammation. This can result in adrenal insufficiency, a condition where the body is unable to produce enough cortisol on its own. Symptoms of adrenal insufficiency include fatigue, weakness, low blood pressure, and difficulty handling stress.
Suppressed Immune System
Another consequence of excess prednisone use is a suppressed immune system. This can make individuals more susceptible to infections and slow down the body's ability to heal. It is important to take precautions to minimize the risk of infections, such as practicing good hygiene and avoiding contact with sick individuals.
Other Potential Risks
In addition to the aforementioned risks, excessive prednisone use can also lead to high blood pressure, elevation of blood sugar levels, cataracts, glaucoma, and mental health issues such as anxiety and depression. Regular monitoring and close supervision by a healthcare professional are crucial when using prednisone to mitigate such risks.
In conclusion, understanding the risks associated with excessive prednisone use is essential. While this medication can be highly effective in managing certain conditions, it should be used judiciously and under careful medical supervision to minimize the potential for adverse effects. Awareness of these risks empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their treatment options and take appropriate measures to protect their health.
Side Effects on the Body
Excessive use of prednisone, a corticosteroid medication, can lead to various side effects on the body. These side effects can range from mild to severe and may require medical attention.
Hormonal Imbalance
Prednisone can disrupt the normal functioning of the endocrine system, leading to hormonal imbalance. This can result in issues such as weight gain, increased appetite, and fluid retention. It can also lead to mood swings, irritability, and changes in sleep patterns. Women may experience irregular menstrual cycles.
Suppressed Immune System
Long-term use of prednisone can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections. It can slow down wound healing and increase the risk of developing certain conditions, such as pneumonia or urinary tract infections.
Bone Loss and Muscle Weakness
Prednisone can cause bone loss and muscle weakness, especially with prolonged use. This increases the risk of developing osteoporosis and fractures. It can also lead to muscle wasting and weakness, making it difficult for individuals to perform everyday activities.
Increased Blood Sugar Levels
One of the most significant side effects of prednisone is the elevation of blood sugar levels. This can lead to the development or worsening of diabetes in individuals who are already at risk. It may also cause increased thirst, frequent urination, and blurred vision.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Prednisone can irritate the lining of the stomach and intestines, leading to gastrointestinal issues such as stomach ulcers, indigestion, and abdominal pain. It can also cause nausea, vomiting, and changes in bowel movements.
It is important to note that these side effects can vary from person to person and depend on the dosage and duration of prednisone use. It is advisable to discuss any concerns or symptoms with a healthcare provider to ensure appropriate management and monitoring of side effects.
Impact on Mental Health
Excessive intake of prednisone can have a significant impact on mental health. This medication belongs to a class of drugs known as corticosteroids, which can affect the levels of certain chemicals in the brain that regulate mood and behavior.
One common side effect of prednisone is mood swings. People taking high doses of prednisone may experience sudden changes in their mood, ranging from euphoria to depression. These mood swings can be intense and unpredictable, making it challenging for individuals to manage and cope with their emotions effectively.
In addition to mood swings, prednisone can also cause anxiety and insomnia. Some individuals may experience increased feelings of restlessness or nervousness, making it difficult to relax and fall asleep. This can lead to a cycle of sleep deprivation and exacerbate feelings of anxiety.
Another mental health issue that can arise from excessive prednisone use is cognitive problems. Some individuals may experience difficulties with concentration, memory, and decision-making. These cognitive impairments can impact daily functioning and lead to frustration and decreased confidence.
It is important for individuals who are prescribed prednisone to be aware of its potential impact on mental health and to communicate any changes or concerns to their healthcare provider. Taking steps to manage stress, engage in self-care activities, and seek support from friends, family, or a mental health professional can also be beneficial in mitigating the impact of prednisone on mental well-being.
Long-Term Consequences
Taking excessive doses of prednisone over a long period of time can lead to a variety of long-term consequences. These consequences can include:
- Osteoporosis: Prolonged use of prednisone can lead to bone loss and an increased risk of developing osteoporosis. This is because prednisone can interfere with the body's ability to absorb calcium, leading to weakened bones.
- Suppressed immune system: Prednisone is known to suppress the immune system, which can make individuals more susceptible to infections and illnesses. Long-term use of prednisone can further weaken the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections.
- Weight gain: Many individuals who take prednisone for long periods of time experience weight gain. This is because prednisone can increase appetite and cause fluid retention in the body.
- Diabetes: Prolonged use of prednisone can lead to the development of diabetes or worsen existing diabetes. This is because prednisone can interfere with the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels.
It is important to note that not everyone who takes prednisone will experience these long-term consequences. The severity and likelihood of these consequences can vary depending on factors such as the dosage and duration of prednisone use, as well as individual factors such as age and overall health. However, it is important to be aware of the potential risks associated with long-term prednisone use and to discuss any concerns with a healthcare professional.
Alternative Solutions
1. Gradually taper off the medication
One alternative solution to mitigate the consequences of taking excessive prednisone is to gradually taper off the medication under the supervision of a healthcare professional. This can help minimize withdrawal symptoms and allow the body to adjust to lower levels of the medication over time.
2. Explore non-pharmacological treatments
Another alternative solution is to explore non-pharmacological treatments that can help manage the underlying condition for which prednisone was prescribed. This may include lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthy diet and exercise regimen, or alternative therapies like acupuncture or yoga.
3. Seek second opinion
If you are concerned about the excessive use of prednisone or the side effects you are experiencing, it may be helpful to seek a second opinion from another healthcare professional. They can provide a fresh perspective and potentially offer alternative treatment options that may be more suitable for your specific needs.
4. Consider complementary therapies
In addition to traditional medical treatments, considering complementary therapies can be an alternative solution. These may include herbal supplements, dietary changes, or other alternative treatments that can help alleviate symptoms or reduce the dependence on prednisone.
5. Engage in a support network
Building a support network of friends, family, or support groups can be an essential alternative solution. They can provide emotional support, share experiences, and offer advice or coping strategies for managing the consequences of taking excessive prednisone.
6. Follow a closely monitored drug regimen
If prednisone is necessary for your condition, closely following a drug regimen under the supervision of a healthcare professional can help minimize the consequences. This includes taking the prescribed dosage, adhering to the recommended duration of treatment, and attending regular check-ups to monitor your response to the medication.
- Gradually tapering off prednisone
- Exploring non-pharmacological treatments
- Seeking a second opinion
- Considering complementary therapies
- Engaging in a support network
- Following a closely monitored drug regimen
Follow us on Twitter @Pharmaceuticals #Pharmacy
Subscribe on YouTube @PharmaceuticalsYouTube


Be the first to comment on "What happens if i take too much prednisone"